Server uptime monitoring tracks the availability and reliability of servers within your infrastructure.
What Is Server Uptime Monitoring?
Server uptime monitoring is the process of continuously tracking the operational status of your servers to ensure optimal performance and availability for users.
With Netdata, you gain access to real-time, high-resolution monitoring that goes beyond basic checks, providing a detailed overview of your entire infrastructure.
Netdata’s monitoring platform sends continuous requests to your servers, gathering key performance metrics such as uptime, response times, and error rates.
The platform provides in-depth visibility into server health, allowing administrators to address potential issues before they escalate, ensuring your systems stay reliable and efficient.
Comparing Server Uptime Monitoring With Other Monitoring Types
While uptime monitoring is essential, it’s just one piece of the broader observability puzzle. To understand where it fits in, it helps to compare it with other monitoring approaches:
Application Performance Monitoring (APM)
APM focuses on analyzing the performance of application code and user transactions. It helps detect slow queries, bottlenecks, and performance issues at the application layer, going beyond just availability.
Synthetic Monitoring
Synthetic monitoring simulates user interactions to test response times and availability from different global locations. It’s proactive and helps ensure user-facing services are functioning before real users encounter issues.
Infrastructure Monitoring
This type involves deeper tracking of physical and virtual hardware performance, including CPU, memory, disk I/O, and network throughput, offering a comprehensive view of the server stack.
Uptime Monitoring’s Role
Uptime monitoring ensures servers and services are reachable and responsive. While not as granular as APM, it’s foundational for identifying availability issues and triggering investigations.
Each monitoring type plays a unique role. Used together, they create a complete observability strategy that improves system reliability and user experience.
The Importance Of Server Uptime Monitoring
Servers are crucial to the operation of many applications and services, making their uptime a critical aspect of overall system performance. Here are some reasons why server uptime monitoring is important:
Consistent Server Availability
Uptime monitoring can show whether a server is consistently available or experiences frequent downtimes. High uptime indicates the server is reliable and available for users, while low uptime may signal potential issues that need to be addressed.
Monitoring Performance Patterns
While server uptime alone doesn’t provide detailed performance data, analyzing the duration and frequency of downtimes can help identify patterns or trends. For example, recurring downtimes during peak hours may indicate capacity issues that need to be addressed.
Proactive Problem Detection
If server uptime monitoring reveals unexpected downtimes or a decreasing uptime trend, it can serve as an early warning sign of potential problems. By monitoring uptime, you can act before issues escalate into more significant disruptions.
Root Cause Analysis
When investigating server downtime, the uptime metric alone may not provide enough information to pinpoint the exact cause. However, it can help narrow down the list of potential issues. For example, if a server experiences sudden downtimes, it may indicate a hardware failure, while frequent short downtimes could suggest software or configuration issues.
Identifying Load Balancing Issues
Uptime data can indirectly indicate load balancing issues if certain servers have significantly lower uptimes than others. This may suggest that those servers are overloaded, and the workload needs to be redistributed more evenly.
Prioritizing Maintenance On Underperforming Servers
Servers with consistently low uptimes or frequent downtimes may require more attention. By identifying these problematic servers through uptime monitoring, resources can be allocated more effectively to address the issues.
Meeting SLAs & Regulatory Compliance
Server uptime data can be used to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements or SLAs that mandate a minimum level of server availability. It provides a measurable and objective metric to track and report.
How Server Uptime Monitoring Works
Automated Checks
Netdata’s monitoring software continuously performs automated checks on your servers, sending regular HTTP requests, pings, and other types of queries to ensure each system is responsive and performing as expected. These checks can be configured to run as frequently as needed, providing instant feedback on the server’s status.
Comprehensive Performance Metrics
Netdata goes beyond simple uptime monitoring by tracking a range of performance indicators such as CPU usage, memory, disk space, and network activity. By measuring these metrics in real time, Netdata enables you to gain actionable insights into server health, helping you detect performance bottlenecks or potential failures.
Custom Thresholds & Alerts
With Netdata, administrators can define custom thresholds for server performance metrics. When a server’s performance deviates from these pre-set standards, the platform triggers alerts. Whether it’s slow response times, high error rates, or unexpected downtime, Netdata ensures you’re instantly notified.
Multi-Channel Notifications
Stay informed with alerts delivered via multiple channels including email, SMS, and integrations with systems like Slack and PagerDuty. Netdata’s flexibility ensures that administrators can choose the notification system that best fits their workflow, ensuring timely responses to server issues.
Centralized Dashboard & Detailed Reports
Netdata provides an intuitive, centralized dashboard that offers real-time and historical insights into your server’s performance. Track trends, detect recurring issues, and make data-driven decisions with ease using our comprehensive reporting tools.
Automated Responses
For advanced server management, Netdata can be configured to trigger automatic responses to certain conditions. Whether it’s restarting services, running custom scripts, or scaling resources in response to increased demand, Netdata enables you to automate corrective actions, reducing downtime and improving overall efficiency.
Best Practices For Effective Uptime Monitoring
To get the most out of server uptime monitoring, it’s essential to follow best practices that maximize coverage, reduce false positives, and help detect real issues early.
Monitor From Multiple Locations
Ensure that uptime checks originate from various geographical regions to capture regional outages or latency issues.
Separate Planned vs Unplanned Downtime
Proper tagging or annotation allows accurate tracking of intentional reboots vs. unexpected failures—making uptime metrics more meaningful.
Set Context-Aware Alert Thresholds
Define thresholds based on the criticality of services. Not every fluctuation needs an alert; focus on deviations that matter.
Integrate With Incident Response Tools
Connect Netdata with systems like PagerDuty or Slack to route alerts directly to the right team, reducing response time.
Regularly Audit & Optimize Monitoring Rules
Review thresholds and alerting rules periodically to ensure they align with current system performance and team workflows.
By following these practices, organizations can improve uptime reliability and gain a clearer understanding of server health.
Managing Planned vs Unplanned Downtime Effectively
Servers often need to be rebooted for various reasons, such as completing software upgrades, installing new system-wide libraries, or updating kernels. These reboots contribute to planned downtime, which is an expected and necessary part of server maintenance.
In the context of server uptime monitoring, it’s essential to differentiate between planned and unplanned downtime. Here’s how the uptime metric can still be useful:
Evaluating Maintenance Efficiency
Analyzing the duration and frequency of planned downtimes can help you evaluate the maintenance processes’ efficiency. For example, if a server consistently takes longer than expected to reboot after software upgrades, this could indicate room for improvement in the maintenance process.
Tracking Unplanned Downtime
By accounting for planned downtime, server uptime monitoring can help you focus on identifying and addressing unplanned downtime events.
SLA Compliance
In many cases, SLAs account for planned downtime and only penalize organizations for unplanned downtime. Monitoring server uptime, including planned downtimes, helps ensure that the organization stays within SLA limits.
Performance Optimization
By tracking the impact of software upgrades, library updates, and kernel changes on server uptime, you can gain insights into how these changes affect system performance and stability.
Server Uptime Monitoring For Cloud VMs (Virtual Machines)
Server uptime monitoring can be helpful for cloud-provided virtual machines (VMs) as well. While cloud providers typically offer higher levels of reliability and redundancy compared to on-premises infrastructure, it’s still essential to monitor the availability and performance of your VMs. Ensuring that your VMs are up and running directly impacts the availability of the applications and services they host.
Additionally in the event of a cloud service disruption or outage, having access to your VMs’ uptime data can help you diagnose issues, assess the impact, and coordinate your incident response efforts.
Why Uptime Monitoring Still Matters In Kubernetes
Kubernetes has built-in features to address many of the server availability issues automatically, but it’s still important to monitor your environment for a complete understanding of the system’s health and performance. Kubernetes is designed to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications, and it includes mechanisms to handle node failures, container restarts, and autoscaling. However, monitoring remains a crucial aspect to ensure that these automated processes are functioning as expected.
Here’s why monitoring, including server uptime monitoring, is still important in a Kubernetes environment:
System-Wide Visibility
While Kubernetes automates many aspects of managing containerized applications, monitoring provides visibility into the health and performance of your cluster. This insight helps you understand how well Kubernetes is managing your environment and identify any potential issues or areas for improvement.
Issue Detection
Even though Kubernetes is designed to handle failures and scale resources automatically, there can still be issues with the underlying infrastructure, such as hardware failures, network problems, or misconfigurations. Monitoring helps detect these issues so that you can address them proactively.
Autoscaling Evaluation
Monitoring the uptime and resource usage of your Kubernetes nodes can help you evaluate the effectiveness of your autoscaling policies and make adjustments if necessary. This ensures that your cluster is optimally scaled to handle changing workloads.
Incident Response
When issues occur in your Kubernetes cluster, having access to monitoring data, including server uptime, can help you diagnose problems, assess the impact, and coordinate your response efforts more effectively.
Compliance & Reporting
Monitoring your Kubernetes environment can help you demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements or service level agreements (SLAs) and provide stakeholders with performance reports and insights.
Simplify Server Uptime Monitoring With Netdata
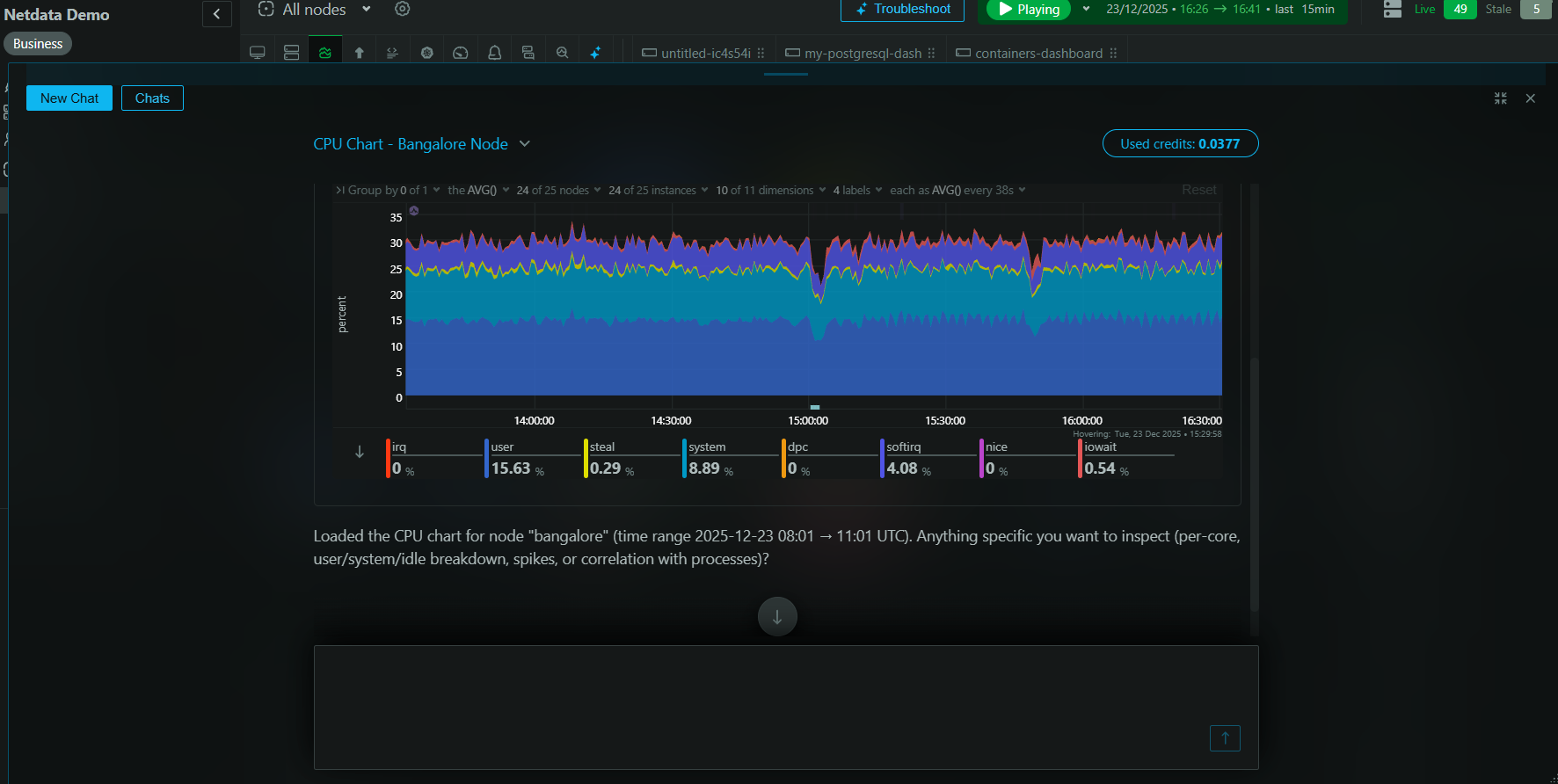
Netdata’s system.uptime chart in the System Overview section allows you to visualise how long each of the nodes in your infrastructure have been successfully running and can be used to trigger alerts when a node restarts or something unexpected happens.

In summary, while server uptime is a single metric, it can still provide valuable insights into the overall health and reliability of servers when analyzed and interpreted correctly. It serves as a starting point for further investigation, and when combined with other metrics, it can provide additional insights for understanding a server’s performance and potential issues.
Server Uptime Monitoring - Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is Considered Good Server Uptime?
A good benchmark for server uptime is 99.9% or higher, which translates to less than 9 hours of downtime per year. Critical systems may aim for 99.99% or more.
Can Uptime Monitoring Detect Slow Servers?
Not directly, but when paired with performance metrics like response time and CPU load, uptime monitoring helps spot servers that are slow or underperforming.
How Often Should Uptime Checks Be Performed?
For production systems, checks every 30 to 60 seconds are common. More frequent checks (e.g., every 10 seconds) are useful for mission-critical infrastructure.
Does Uptime Monitoring Work In Kubernetes?
Yes. Even though Kubernetes handles restarts and autoscaling, uptime monitoring adds visibility and helps verify that automation is working as expected.
How Does Uptime Monitoring Help With Incident Response?
Uptime monitoring provides immediate alerts when servers go down, allowing teams to act quickly. It also offers historical data to help diagnose root causes and prevent repeat incidents.