Couchbase Monitoring
What Is Couchbase?
Couchbase is a distributed NoSQL cloud database ideal for interactive web and mobile applications. Designed to support massive data volumes and a large number of users, Couchbase provides core database functions while enhancing performance through its advanced memory-first architecture.
Monitoring Couchbase With Netdata
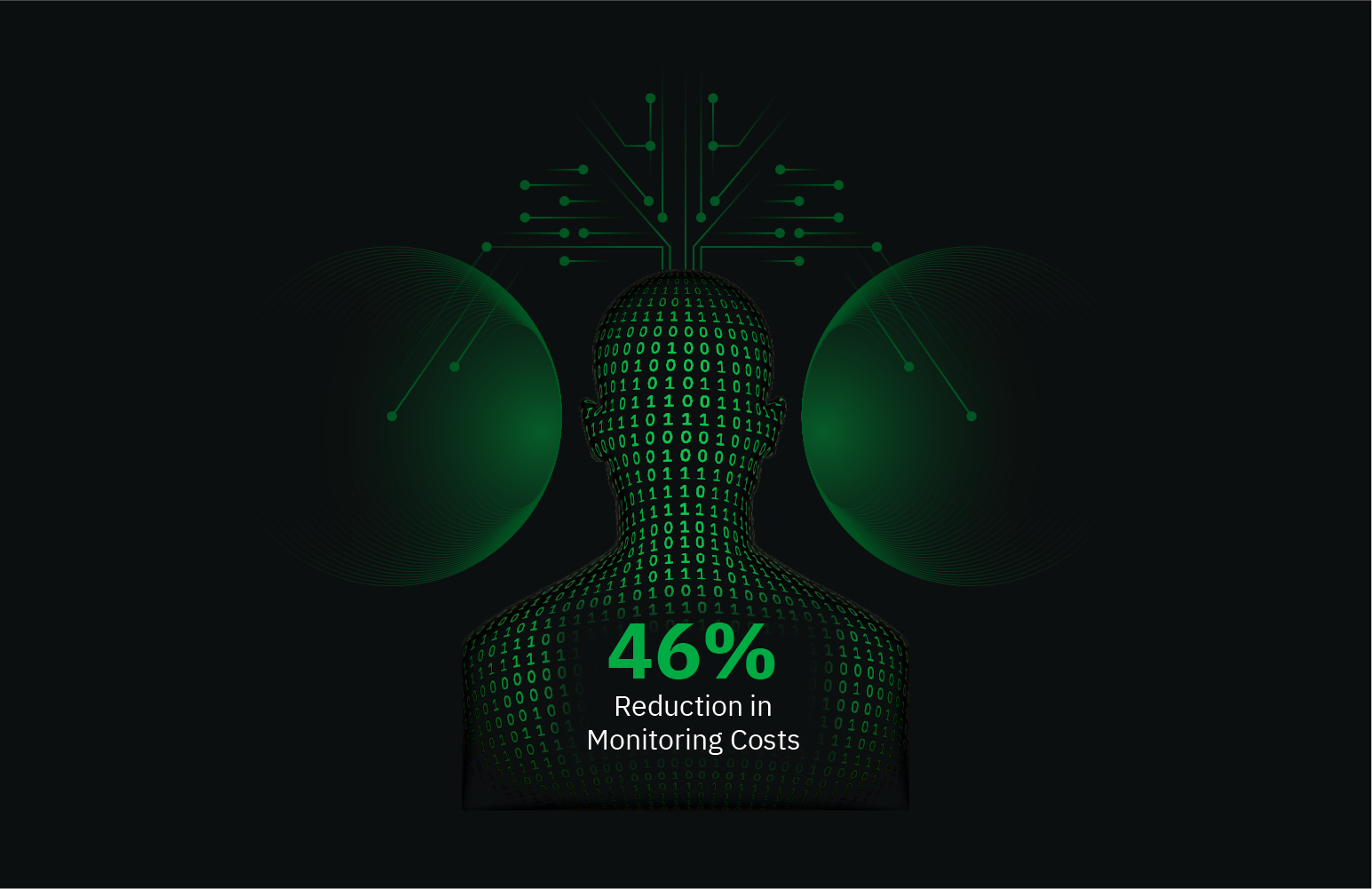
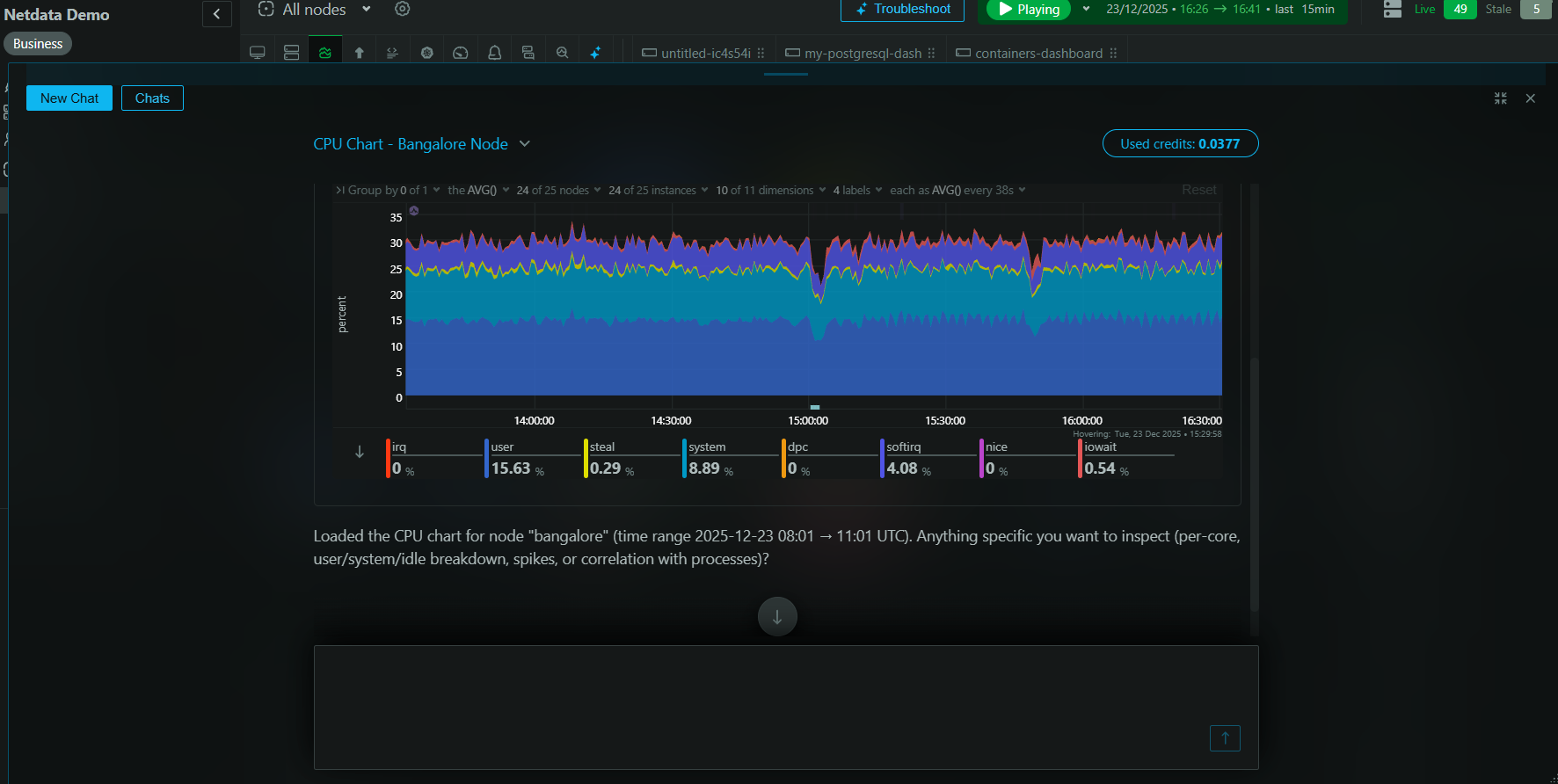
Monitoring Couchbase’s health and performance is essential to maintaining its operations-efficiently. With Netdata, you can seamlessly integrate Couchbase monitoring and get real-time insights into vital metrics. Netdata’s intuitive dashboard provides detailed metrics, enabling you to keep a close watch on Couchbase’s performance.
Find out more in the Couchbase collector documentation.
Why Is Couchbase Monitoring Important?
Monitoring Couchbase is critical in ensuring resource optimization, identifying bottlenecks, and maintaining high availability. Continuous monitoring helps prevent data loss and downtime and enables quick recovery from potential failures, offering a robust and reliable database environment for your applications.
What Are The Benefits Of Using Couchbase Monitoring Tools?
Using tools for monitoring Couchbase, like Netdata, provides actionable insights into database performance and health. These tools facilitate capacity planning, provide historical data analysis, and can alert teams to potential issues before they escalate, ensuring optimal database performance and customer satisfaction.
Understanding Couchbase Performance Metrics
Monitoring key Couchbase performance metrics helps in diagnosing and troubleshooting database issues efficiently. Below are the crucial metrics collected by Netdata:
- Quota Percent Used Per Bucket: Indicates the percentage of allocated memory quota used by each bucket.
- Operations Per Second Per Bucket: Measures the operations processed per second for each bucket.
- Disk Fetches Per Bucket: Represents the number of disk fetches for each bucket, pointing to potential performance issues.
- Item Count Per Bucket: Displays the total number of items stored per bucket.
- Disk Used Per Bucket: Monitors the amount of disk space used per bucket.
- Data Used Per Bucket: Indicates how much data is being used per bucket.
- Memory Used Per Bucket: Tracks the memory consumption per bucket.
- Number Of Non-Resident Items Per Bucket: Counts the items not cached in memory per bucket.
| Metric Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Quota Percent Used Per Bucket | Percentage of allocated memory used by bucket |
| Operations Per Second Per Bucket | Number of operations per second per bucket |
| Disk Fetches Per Bucket | Number of disk fetches per bucket |
| Item Count Per Bucket | Total number of items per bucket |
| Disk Used Per Bucket | Disk space used per bucket |
| Data Used Per Bucket | Amount of data used per bucket |
| Memory Used Per Bucket | Memory consumption per bucket |
| Non-Resident Items Per Bucket | Items not cached in memory per bucket |
Advanced Couchbase Performance Monitoring Techniques
Utilize advanced features like multi-instance support with Netdata to monitor multiple Couchbase instances simultaneously. Tailor your monitoring setup to capture specific metrics using configurable options to fine-tune data collection frequency and response times.
Diagnose Root Causes Or Performance Issues Using Key Couchbase Statistics & Metrics
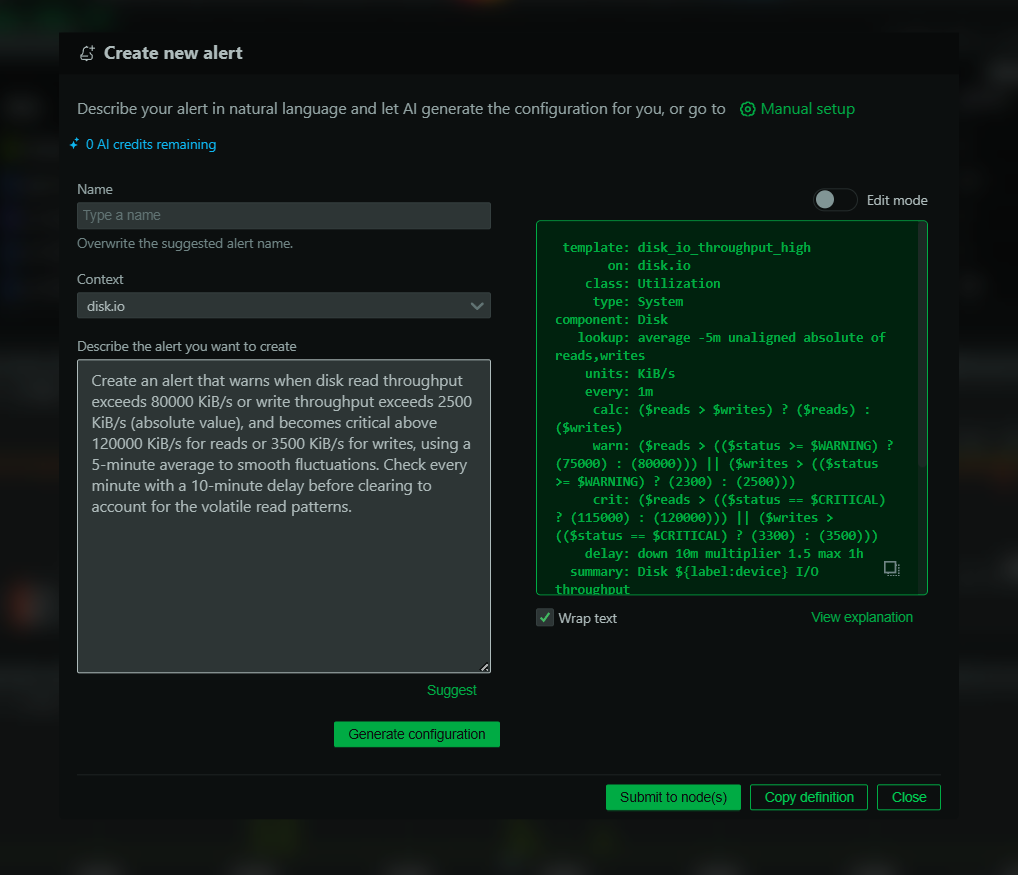
Understanding the real-time and historical data captured by monitoring tools enables DevOps teams to identify patterns, diagnose issues swiftly, and apply the necessary fixes. By leveraging Netdata’s alerts, you can preemptively address issues before they impact service delivery.
Want to see how easy it is to monitor Couchbase with Netdata? Check out the Live Demo or Sign Up for a Free Trial.
FAQs
What Is Couchbase Monitoring?
Couchbase monitoring involves tracking crucial performance metrics of Couchbase databases to ensure they run efficiently and effectively.
Why Is Couchbase Monitoring Important?
Monitoring is crucial for optimizing resources, preventing data loss, ensuring uptime, and maintaining high availability.
What Does A Couchbase Monitor Do?
A Couchbase monitor continuously collects, tracks, and reports on key performance metrics and system health indicators.
How Can I Monitor Couchbase In Real Time?
Using Netdata, you can monitor Couchbase in real-time with an easy setup, an intuitive dashboard, and comprehensive metrics.