NSD Monitoring
What Is NSD?
NSD is an authoritative DNS name server developed by NLnet Labs. It is renowned for its high performance, robust security measures, and support for various DNS standards. NSD is a cornerstone for businesses looking for a reliable DNS solution to ensure smooth and secure network communication. You can find more in-depth information on the NSD official documentation.
Monitoring NSD With Netdata
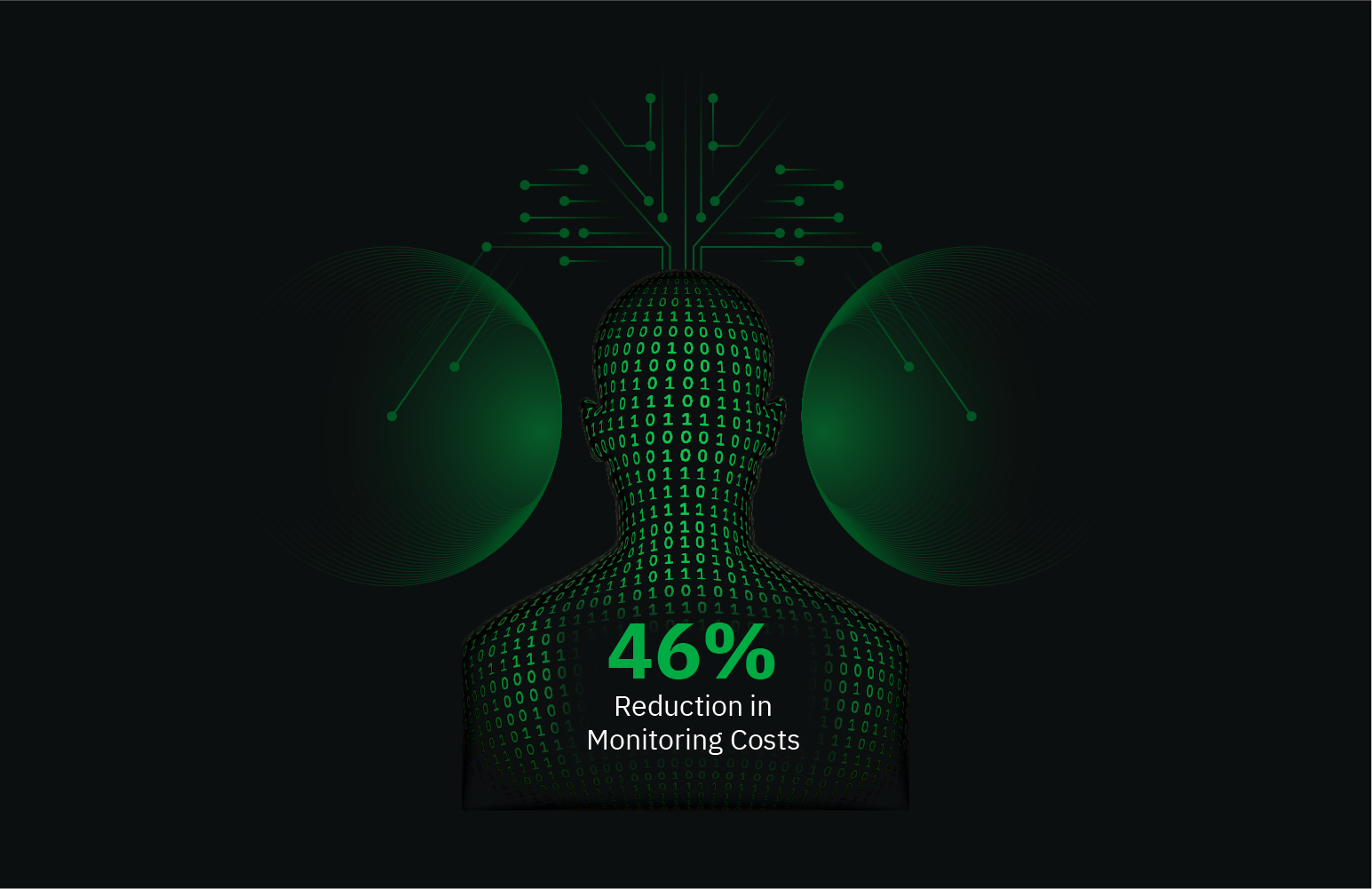
Monitoring NSD effectively is crucial to maintaining optimal server performance and securing uptime. Netdata offers a comprehensive NSD monitoring tool that easily integrates with your system to provide in-depth insights into your DNS server’s performance. By leveraging Netdata, you can continuously monitor NSD metrics in real time, enabling swift diagnosis and resolution of potential issues.
To see NSD monitoring in action, check out Netdata’s Live Demo.
Why Is NSD Monitoring Important?
Monitoring NSD is essential for maintaining a healthy DNS infrastructure. By keeping a close eye on real-time metrics, you can ensure efficient query handling, prevent security breaches, and optimize resource usage. Effective NSD monitoring can help preempt downtime, enhance server performance, and ensure seamless network operations.
What Are The Benefits Of Using NSD Monitoring Tools?
Employing NSD monitoring tools, like Netdata, provides:
- Real-Time Insights: Instant data on query performance, transfer rates, error rates, and more.
- Security Monitoring: Keep track of errors, unauthorized access attempts, and query refusal rates.
- Resource Optimization: Monitor database sizes, memory usage, and overall performance metrics.
- Operational Efficiency: Quick identification and resolution of potential issues before they escalate.
Understanding NSD Performance Metrics
Monitoring NSD requires understanding key performance metrics. Here are some essential metrics that Netdata’s NSD module tracks:
nsd.queries
- Description: Tracks the number of queries received.
- Unit: queries/s
nsd.queries_by_type
- Description: Categorizes queries by type, such as A, NS, CNAME, etc.
- Unit: queries/s
nsd.queries_by_protocol
- Description: Breaks down queries by transport protocol like UDP, TCP, etc.
- Unit: queries/s
nsd.answers_by_rcode
- Description: Monitors the response code distribution of answers.
- Unit: answers/s
nsd.uptime
- Description: Shows the server’s uptime.
- Unit: seconds
| Metric Name | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| nsd.queries | Monitors inbound DNS queries | queries/s |
| nsd.queries_by_type | Categorizes DNS queries by specific type codes | queries/s |
| nsd.queries_by_protocol | Tracks query distribution by protocol (e.g., UDP) | queries/s |
| nsd.answers_by_rcode | Monitors response codes for DNS answers | answers/s |
| nsd.uptime | Tracks the server uptime | seconds |
Advanced NSD Performance Monitoring Techniques
Advanced monitoring can involve analyzing trends over time, setting custom alerts for unusual activity, and utilizing diagnostic data to refine DNS configurations. Netdata empowers users with customizable alerts and historical data views, facilitating proactive management of DNS services.
Diagnose Root Causes Or Performance Issues Using Key NSD Statistics & Metrics
Leveraging Netdata’s comprehensive NSD statistics, you can diagnose root causes by tracking anomalies in query types, error codes, or transfer rates. Such monitoring allows for informed troubleshooting and strategic adjustments, reducing downtime and enhancing DNS service reliability.
To start monitoring NSD effectively, Sign Up to Netdata for a free trial and explore how detailed insights can be leveraged to maintain a robust DNS infrastructure.
FAQs
What Is NSD Monitoring?
NSD monitoring refers to observing and analyzing metrics relevant to the operation of the NSD server for ensuring its reliability, performance, and security.
Why Is NSD Monitoring Important?
It ensures the DNS service’s optimal performance, prevents outages, and enhances system security by identifying unusual behaviors and potential threats.
What Does An NSD Monitor Do?
An NSD monitor tracks various performance attributes such as query types, protocols, response codes, uptime, and errors to provide actionable insights into the DNS server’s health.
How Can I Monitor NSD In Real Time?
Real-time monitoring of NSD can be achieved using tools like Netdata, which provides instantaneous data analysis and visualization capabilities for dynamic and accurate server performance monitoring. Try it live!